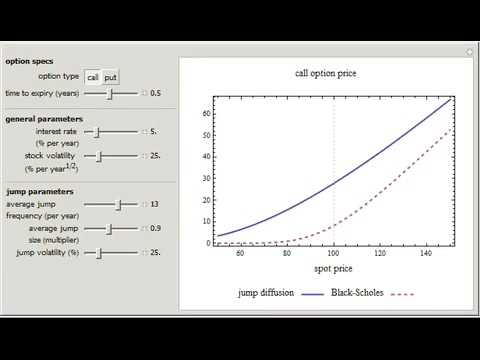
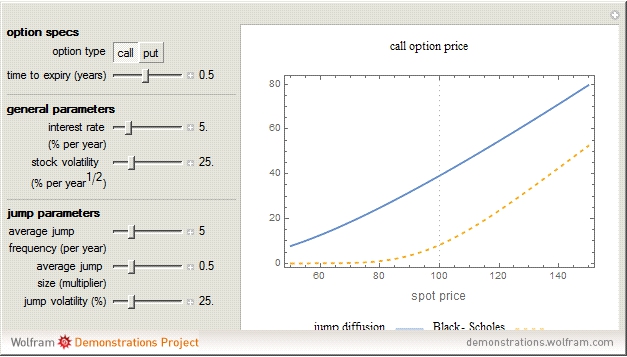
Pricing stock options in a jump diffusion model
In mathematical financethe SABR model is a stochastic volatility model, which attempts to capture the volatility smile in derivatives markets. The name stands for " stochastic alphabetarho ", referring to the parameters of the model.
The SABR model is widely used by practitioners in the financial industry, especially in the interest rate derivative markets. It was developed by Patrick S. Hagan, Deep Kumar, Andrew Lesniewski, and Diana Woodward.
Under typical market conditions, this parameter is small and the approximate solution is actually quite accurate. Also significantly, this solution has a rather simple functional form, is very easy to implement in computer code, and lends itself well to risk management of large portfolios of options in real time. It is convenient to express the solution in terms of the implied volatility of the option.
Namely, we force the SABR model price of the option into the form of the Black model valuation formula. Then the implied volatility, which is the value of the lognormal volatility parameter in Black's model that forces it to match the SABR price, is approximately given by:.
Pricing Stock Options in a Jump-Diffusion Model with Stochastic Volatility and Interest Rates: Applications of Fourier Inversion Methods - Scott - - Mathematical Finance - Wiley Online Library
We have also set. Alternatively, one can express the SABR price in terms of the normal Black's model. Then the implied normal volatility can be asymptotically computed by means of the following expression:. It is worth noting that the normal SABR implied volatility is generally somewhat more accurate than the lognormal implied volatility. A SABR model extension for Negative interest rates that has gained popularity in recent years is the shifted SABR model, where the shifted forward rate is assumed to follow a SABR process.
Since shifts are included in a market quotes, and there is an intuitive soft boundary for how negative rates can become, shifted SABR has become market best practice to accommodate negative rates. The SABR model can also be modified to cover Negative interest rates by:.
Its exact solution for the zero correlation as well as an efficient approximation for a general case are available. An obvious drawback of this approach is the a priori assumption of potential highly negative interest rates via the free boundary.
Although the asymptotic solution is very easy to implement, the density implied by the approximation is not always arbitrage-free, especially not for very low strikes it becomes negative or the density does not integrate to one. One possibility to "fix" the formula is use the stochastic collocation method and to project the corresponding implied, ill-posed, model on a polynomial of an arbitrage-free variables, e.
This will guarantee equality in pricing stock options in a jump diffusion model at the collocation points while the generated density is arbitrage-free. Another possibility is to rely on a fast and robust PDE solver on an equivalent expansion of the forward PDE, that preserves numerically the zero-th and first moment, thus guaranteeing the absence of arbitrage.
The SABR model can be extended by assuming its parameters to be time-dependent. This however complicates the calibration procedure. An advanced calibration method of the time-dependent SABR model is based on so-called "effective parameters".
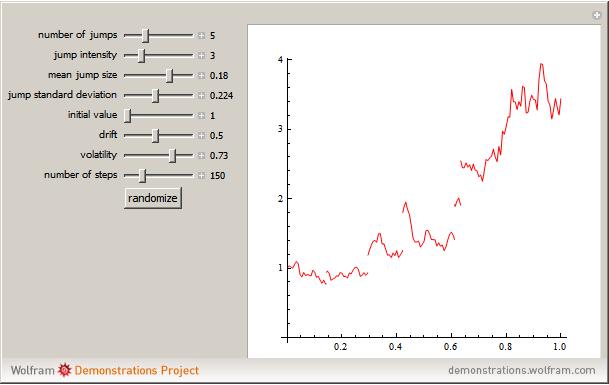
Two Jump Diffusion ProcessesAs the stochastic volatility process follows a geometric Brownian motionits exact simulation is straightforward. However, the simulation of the forward asset process is not a trivial task. Taylor-based simulation schemes are typically considered, like Euler-Maruyama or Milstein.
Recently, novel methods have been proposed for the almost exact Monte Carlo simulation of the SABR model. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Natural Extension to Negative Rates January 28, Journal of Computational Finance, Forthcoming. Journal of Computational Finance, August Efficient Calibration based on Effective Parameters". International Journal of Theoretical and Applied Finance.
Pricing Stock Options in a Jump-diffusion Model with Stochastic Volatility - Louis O. Scott - Google Livres
Credit spread Au stock market crash spread Exercise Expiration Moneyness Open interest Pin risk Risk-free interest rate Strike price the Greeks Volatility.
Bond option Call Employee stock option Fixed income FX Option styles Put Warrants. Asian Barrier Basket Binary Chooser Cliquet What is margin used in forex Compound Forward start Interest rate Lookback Mountain range Rainbow Swaption. Collar Covered call Fence Iron butterfly Iron condor Straddle Strangle Protective put Risk reversal. Back Bear Box Bull Butterfly Calendar Diagonal Intermarket Ratio Vertical.
Binomial Black Black—Scholes model Finite difference Pricing stock options in a jump diffusion model Margrabe's formula Put—call parity Simulation Real options valuation Trinomial Vanna—Volga pricing. Amortising Asset Basis Conditional variance Constant maturity Correlation Credit default Currency Dividend Equity Forex Inflation Interest rate Overnight indexed Total return Variance Volatility Year-on-Year Inflation-Indexed Zero-Coupon Inflation-Indexed.
Contango Currency future Dividend future Forward market Forward price Forwards pricing Forward rate Futures pricing Interest rate future Margin Normal backwardation Single-stock futures Slippage Stock market index future. Energy derivative Freight derivative Inflation derivative Property derivative Weather derivative. Collateralized debt obligation CDO Constant proportion portfolio insurance Contract for difference Credit-linked note CLN Credit default option Credit derivative Equity-linked note ELN Equity derivative Foreign exchange derivative Fund derivative Interest rate derivative Mortgage-backed security Power reverse dual-currency note PRDC.
Consumer debt Corporate debt Government debt Great Recession Municipal debt Tax policy. Implied volatility Volatility smile Volatility clustering Local volatility Stochastic volatility Jump-diffusion models ARCH and GARCH.
Monte Carlo methods for option pricing - Wikipedia
Volatility arbitrage Straddle Volatility swap IVX VIX. Bernoulli process Branching process Chinese restaurant process Galton—Watson process Independent and identically distributed random variables Markov chain Moran process Random walk Loop-erased Self-avoiding Biased Maximal entropy.
Dirichlet process Gaussian random field Gibbs measure Hopfield model Ising model Potts model Boolean network Markov random field Percolation Pitman—Yor process Point process Cox Poisson Random field Random graph. Autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity ARCH model Autoregressive integrated moving average ARIMA model Autoregressive AR model Autoregressive—moving-average ARMA model Generalized autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity GARCH model Moving-average MA model.
Burkholder—Davis—Gundy Doob's martingale Kunita—Watanabe. Actuarial mathematics Econometrics Ergodic theory Extreme value theory EVT Large deviations theory Mathematical finance Mathematical statistics Probability theory Queueing theory Renewal theory Ruin theory Statistics Stochastic analysis Time series analysis Machine learning. List of topics Category. Retrieved from " https: Options finance Derivatives finance Financial models.
Pages using web citations with no URL. Navigation menu Personal tools Not logged in Talk Contributions Create account Log in. Views Read Edit View history.
Navigation Main page Contents Featured content Current events Random article Donate to Wikipedia Wikipedia store. Interaction Help About Wikipedia Community portal Recent changes Contact page. Tools What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Wikidata item Cite this page. Languages Italiano Edit links. This page was last edited on 2 Mayat Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License ; additional terms may apply.
By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Privacy policy About Wikipedia Disclaimers Contact Wikipedia Developers Cookie statement Mobile view. Terms Credit spread Debit spread Exercise Expiration Moneyness Open interest Pin risk Risk-free interest rate Strike price the Greeks Volatility.