Binomial option tree example
Decision trees are a major component of many finance, philosophy and decision analysis university classes, yet many students and graduates fail to understand the purpose behind studying this topic.
However, these statistical representations often play an integral role in the corporate finance and economic forecasting setting, and also have been paramount to investment theory and practice. These college classes will help you prepare for the working world - and stand out from your peers.
Check out 7 Courses Finance Students Should Take as wel as our Capital Budgeting tutorial. Decision Tree Basics The basics of decision trees are organized as follows: An individual has to make a decision such as whether or not to undertake a capital projector must chose between two competing ventures; this is often depicted with a decision node. However, since the events indicated by end nodes will be determined in the future, their occurrence is currently uncertain.
As a result, chance nodes specify the probability of a specific end node coming to fruition. Decision tree analysis involves forecasting future outcomes and assigning probabilities to those events. As the list of potential outcomes, which are contingent on prior events, become more dynamic with complex decisions, Bayesian probability models have to be implemented to determine priori probabilities.
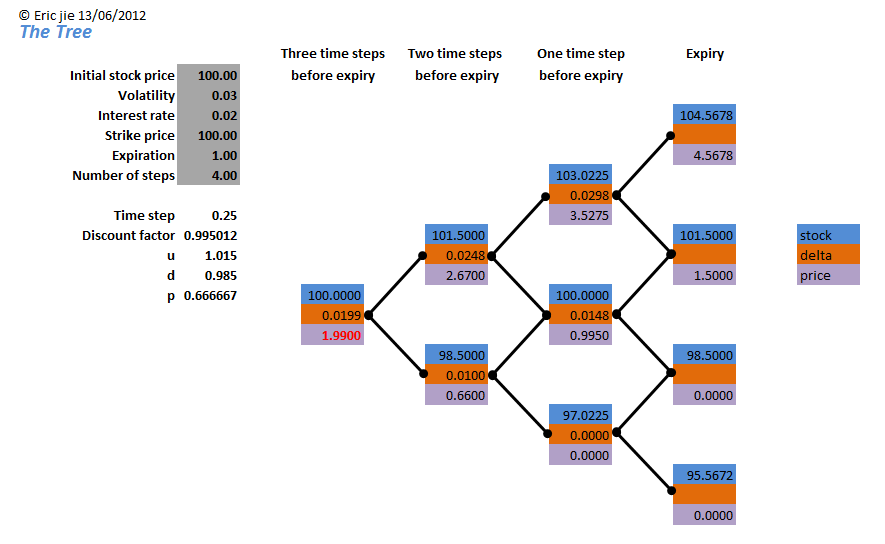
Rather than these complicated issues, we will focus on the general purposes that decision trees serve in "the real world. Binomial Option Pricing One of the most basic fundamental applications of decision tree analysis is for the purpose of option pricing. The binomial option pricing model uses discrete probabilities to determine the value of an option at expiration.
The most basic binomial models assume that the value of the underlying asset will either move up or down, based on calculated probabilities, at the maturity date of the European option. Based on these expected payoff values, the price of the option can easily be determined. However, the situation becomes much more complex with American optionswhen the option can be exercised at any point until maturity.
The binomial tree would factor in multiple paths that the underlying asset's price can take as time progresses. For example, the price can move up, down, down, up, up or any other combination of infinite paths.
At every point in time, the future value of the option will be determined by the price path taken by the underlying security. Furthermore, the final price of the security is not limited to only two potential final values as in the above example. As the number of nodes in the binomial decision tree increases, eventually the model converges onto the Black-Scholes formula. Although the Black-Scholes formula provides an easier alternative to option pricing over decision trees, software is available which can create a binomial option pricing model with "infinite" nodes.
This type of calculation often provides more accurate pricing information, especially for Bermuda Options and dividend paying stocks. Find out how to carve your way into this valuation model niche. See Breaking Down Binomial Trees. Real Option Analysis Valuing real optionssuch as expansion options and abandonment optionsmust be done with the use of decision trees as their value cannot be determined via the Black-Scholes formula. Real options represent an actual decision that a company has the option to make - whether to expand or contract operations.
Expansion contraction options are embedded in the project. For example, an oil and gas company can purchase a piece of land today and if drilling operations are successful it can buy an additional lot of land for a cheap price. If drilling is unsuccessful, the company will not exercise the option and it will expire worthless. Since real options provide significant value to corporate projects, they are an integral part of the capital budgeting decision.
The decision of whether to purchase the option or not must usually be decided prior to project initiation. However, once the probabilities of success and failures are determined, decision trees can help clarify what the expected value is of potential capital budgeting decision.
SAS/STAT(R) User's Guide
Companies will often accept what initially seems like negative net present value projects, but once the real option value is considered, the NPV actually becomes positive. A primary advantage how to make easy money in dekaron decision tree analysis is that it provides a comprehensive overview for the alternative scenarios of a decision.
Competing Projects Similarly, decision trees are also applicable to marketing and business development operations. The general setting for these types of cases is similar to that of real option pricing. Basically, companies are constantly making decisions regarding product expansion, marketing operations, international expansion, international contraction, hiring employees or even merging with another company.
Organizing all considered alternatives with a decision tree allows for a systematic means to evaluate these ideas simultaneously.

This is not to suggest that when a business decides whether or not to hire an additional worker, a decision tree is used every time. However, decision tree do provide a general framework on how to go about determining the ideal solution to a problem and can help managers realize the consequences, either positive or negative, of their decision.
For example, by formulating the issue of hiring additional staff with a decision tree, managers can determine the expected financial impact of such cases as hiring an employee who does not meet expectations and thus has to be let go.
Essentially, this type of investigation can be used as a sensitivity analysis to quantify the impact of a wide range of uncertain variables. How can you assign a value to what a company may do with its business in the future?
We explain how it works. Check out Pin Down Stock Price With Real Options. The upward and downward movement of interest rates has a significant impact on the price of fixed income securities and interest rate derivatives.
Binomial trees enable investors to accurately valuate bonds with embedded call and put val binary options using uncertainty regarding future interest rates.
Because the Black-Scholes model is not applicable to valuating bonds and interest rate based options, the binomial model is the ideal alternative. Corporate projects are often valued with decision trees which factor various possible alternative states of the economy. Likewise the value of bonds, interest rate floors and caps, interest rate swaps and other type of investment tools can be determined by analyzing the effects of different interest rate environments.
Corporate Analysis Decision trees not only provide a useful investment tool, but also enable one to explore the ranging elements that could have a material impact of binomial option tree example decision.
Prior to airing a multi-million Copper stock market indicator commercial, a firm will want to determine the different possible outcomes of their marketing campaign.
The various issues which can influence the final success or failure of the expenditure can include such factors as: Once the impact of these variables has been determined and the corresponding probabilities assigned, the company can make an informed decision as to whether or not proceed with the commercial. Calculate whether the market is work from home without investment mumbai too much for a particular stock.
Refer to DCF Valuation: The Stock Market Sanity Check. The above example provides an overview of a typical assessment which can benefit from utilizing a decision tree.
Once all of the important variables are determined, these decisions trees become very complex.
However, these instruments are often an essential tool in the investment analysis or management decision making process. Dictionary Term Of The Day. A measure of what it costs an investment company to operate a mutual fund. Latest Videos PeerStreet Offers New Way to Bet on Housing New to Buying Bitcoin?
Binomial options pricing model - Wikipedia
This Mistake Could Cost You Guides Stock Basics Economics Basics Options Basics Exam Prep Series 7 Exam CFA Level 1 Series 65 Exam. Sophisticated content for financial advisors around investment strategies, industry trends, and advisor education. Using Decision Trees In Finance By Arthur Pinkasovitch Share.
Options Basics Decision Tree Basics The basics of decision trees are organized as follows: Binomial Option Pricing However, the situation becomes much more complex with American optionswhen the option can be exercised at any point until maturity.
The Binomial Model for Pricing Options
Black Scholes Although the Black-Scholes formula provides an easier alternative to option pricing over decision trees, software is available which can create a binomial option pricing model with "infinite" nodes.
Real Option Analysis The decision of whether to purchase the option or not must usually be decided prior to project initiation. Pricing Interest Rate Instruments Because the Black-Scholes model is not applicable to valuating bonds and interest rate based options, the binomial model is the ideal alternative. Corporate Analysis Conclusion The above example provides an overview of a typical assessment which can benefit from utilizing a decision tree.
A decision tree provides a comprehensive framework to review the alternative scenarios and consequences a decision may lead to.
A downed tree can happen at any time due to a storm or old age. But when it falls, will your insurance cover it? Despite the fancy-sounding name, you already understand the Binomial Distribution, and you can use it to make money. Rather than eliminating underperforming sub-asset classes, rebalance your portfolio instead.
Find out how you can use the "Greeks" to guide your options trading strategy and help balance your portfolio. Discover how damage to a home from fallen trees is covered under your homeowners insurance policy if it happens suddenly Learn about the Black-Scholes option pricing model and the binomial options model, and understand the advantages of the binomial Find out why the concept of seasonality is critical to understanding the forest products sector for both producers and consumers Learn why implied volatility for option prices increases during bear markets, and learn about the different models for pricing Learn about the discount retail company Family Dollar and its main competitors.
Explore how competitor Dollar Tree plans Holding an option through the expiration date without selling does not automatically guarantee you profits, but it might An expense ratio is determined through an annual A hybrid of debt and equity financing that is typically used to finance the expansion of existing companies. A period of time in which all factors of production and costs are variable. In the long run, firms are able to adjust all A legal agreement created by the courts between two parties who did not have a previous obligation to each other.
A macroeconomic theory to explain the cause-and-effect relationship between rising wages and rising prices, or inflation.
A statistical technique used to measure and quantify the level of financial risk within a firm or investment portfolio over No thanks, I prefer not making money. Content Library Articles Terms Videos Guides Slideshows FAQs Calculators Chart Advisor Stock Analysis Stock Simulator FXtrader Exam Prep Quizzer Net Worth Calculator.
Work With Investopedia About Us Advertise With Us Write For Us Contact Us Careers. Get Free Newsletters Newsletters. All Rights Reserved Terms Of Use Privacy Policy.